Sun and air? Study the seaside image for a few seconds . Try to describe it: You might say that the image shows : A calm sea, clear blue sky, bright sunshine and a perfectly smooth beach. You could describe it in terms of the states of matter visible: SOLID Sand LIQUID Sea GASAirGAS and PLASMASun But as a chemist you might be as...
Sun and air? Study the seaside image for a few seconds . Try to describe it: You might say that the image shows : A calm sea, clear blue sky, bright sunshine and a perfectly smooth beach. You could describe it in terms of the states of matter visible: SOLID Sand LIQUID Sea GASAirGAS and PLASMASun As a chemistry student you might be...
Sun and air Study the seaside image for a few seconds . Try to describe it: You might say that the image shows : A calm sea, clear blue sky, bright sunshine and a perfectly smooth beach. You could describe it in terms of the states of matter visible: SOLID Sand LIQUID Sea GASAir GAS + PLASMASun But as a chemist y...
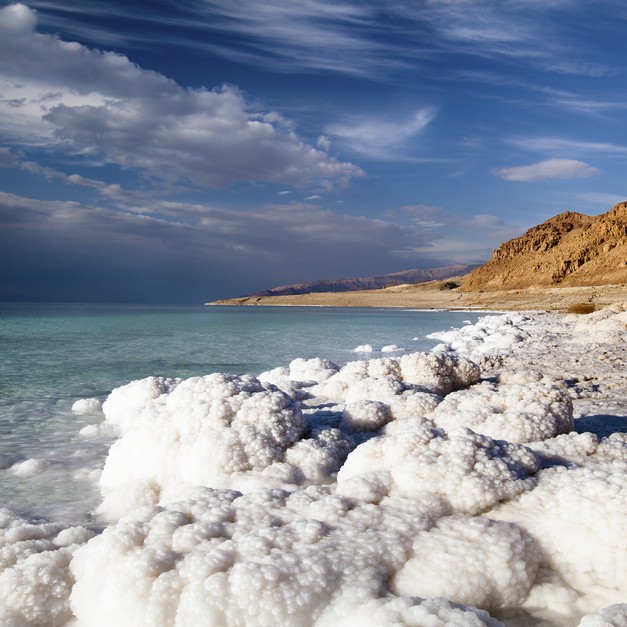
The Dead Sea is below sea level, this means that it does not drain so that although the water evaporates, the salt will stay, this means that the dead sea is a saturated solution. You can see this because salt crystals appear around the shore line. The oceans become salty for the same reason - soluble salts are washed in to the oceans by rive...
Crude oil is a major source of raw material for the petrochemical industry.
Many chemical reactions can be reversed. When this happens we can describe a forward reaction and a back reaction. Sometimes, when in a closed system, the forward and back reaction take place at equal rates. When this happens an Equilibrium is established Students should: 3.17 know that some reactions are reversib...
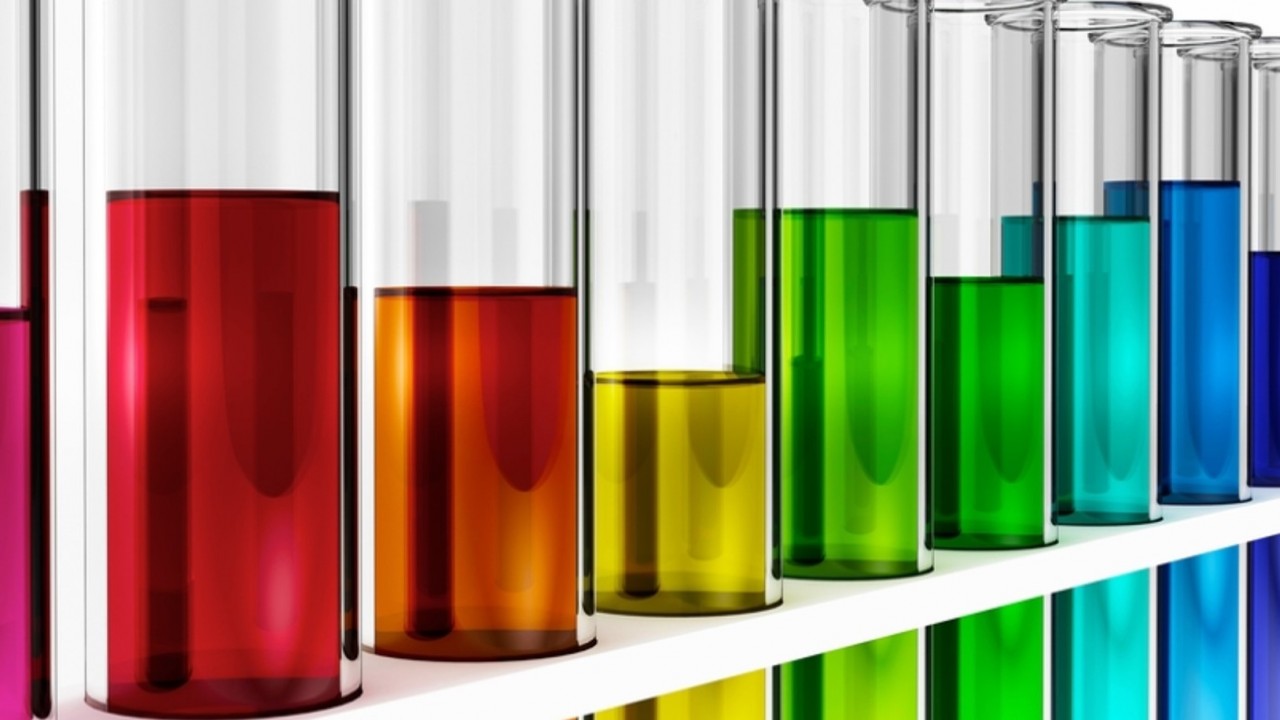
Students should: 1.3 understand how the results of experiments involving the dilution of coloured solutionsand diffusion of gases can be explained This classic demonstration is used to demonstrate diffusion rates QuestionsAnswers in this reaction the two reactants are ammonia and hydrogen chloride write down the formula of each of these compo...
3.1 Energetics Students should: 3.1 know that chemical reactions in which heat energy is given out are described asexothermic, and those in which heat energy is taken in are described as endothermic Every chemical reaction has an accompanying change in energy. Some reactions release energy to the surroundings and are known as Exothermic...
Enter your text here ... IntroductionPearson specification A lot of everyday substances including some foods contain Acids. You can find alkalis amongst a number of common cleaning products. Acids are neutralised by alkalis to form salts and water. Here we consider the ways in which these reactions can be used...
4.29. Handle with care The alcohols are another homologous series like the alkanes and the alkenes. Alcohols contain a functional group made up of an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom. Ethanol is one member of the alcohol series. This is the alcohol in alcoholic drinks. Alcohols are good at dissolving things and are therefo...
4.23 Meet the alkenes The Alkenes are another Homologous series of Hydrocarbons. They differ from the Alkanes because they contain in their molecules at least one double bond between two of the carbon atoms. Because of their double bonds, the alkenes are more reactive than the alkanes and thus they are useful for making new compound...
4.19 Some saturated hydrocarbons The Alkane series is a family of hydrocarbons. The technical name for this sort of "family" is a "homologous series" The alkane molecules contain atoms of hydrogen and carbon only. The general formula for the alkanes is CnH2n+2 Assumed background knowledge 4.1 - 4.7 O...
4.19 Some saturated hydrocarbons The Alkane series is a family of hydrocarbons. The technical name for this sort of "family" is a "homologous series" The alkane molecules contain atoms of hydrogen and carbon only. The general formula for the alkanes is CnH2n+2 4.19- 4.21 Activity 1. From one to ...
Organic chemistry is concerned with the compounds of the element carbon. Here we introduce the basic principles of this huge topic.
IntroductionPearson Specification Analytical chemistry involves the identification of chemical substances using a variety of methods. Although modern technology has enabled chemists to analyse and identify a huge range of substances very quickly and accurately some simple test tube reactions can still be quicker and cheaper to perform. 2....
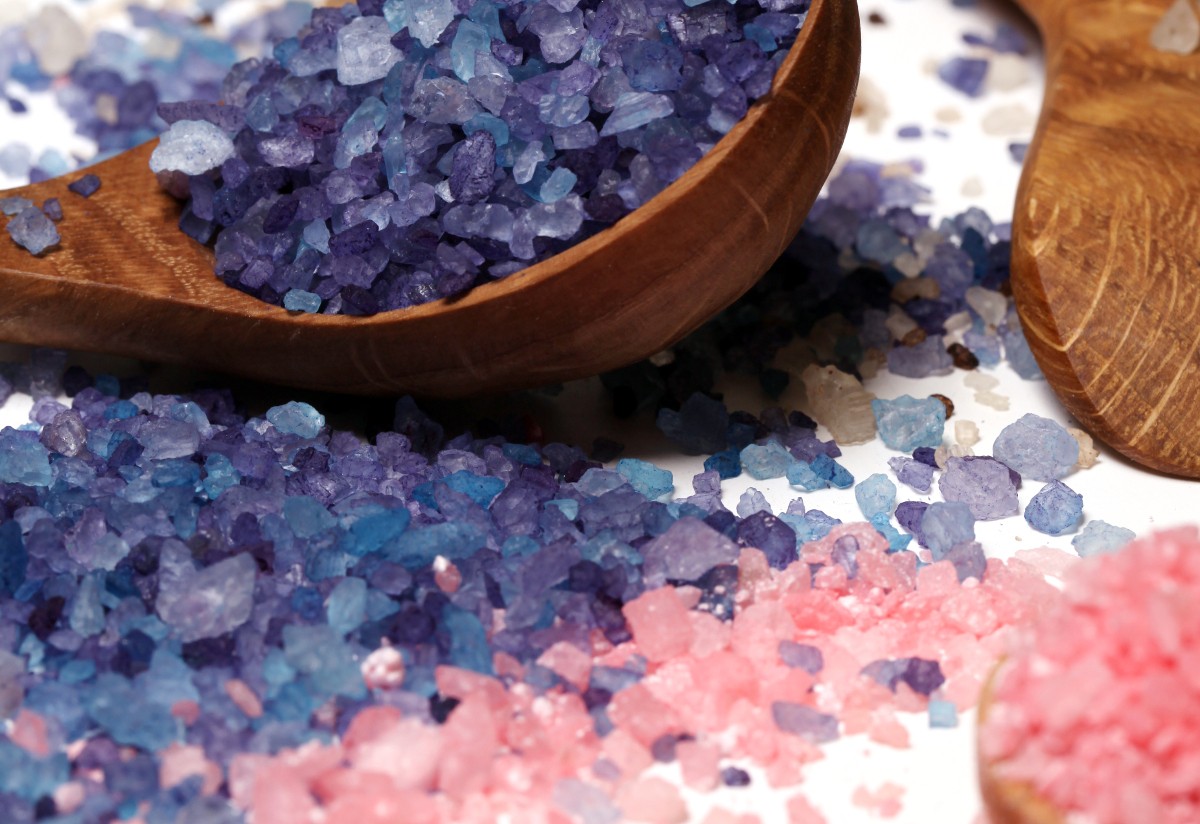
2.34 Defining salts Common "table" salt ( sodium chloride) is found dissolved in large quantities in seawater. Sodium Chloride is just one example of the many compounds which can be called salts. Most salts are crystalline ionic compounds A salt is defined as : A compound resulting from a chemical reaction of an acid...
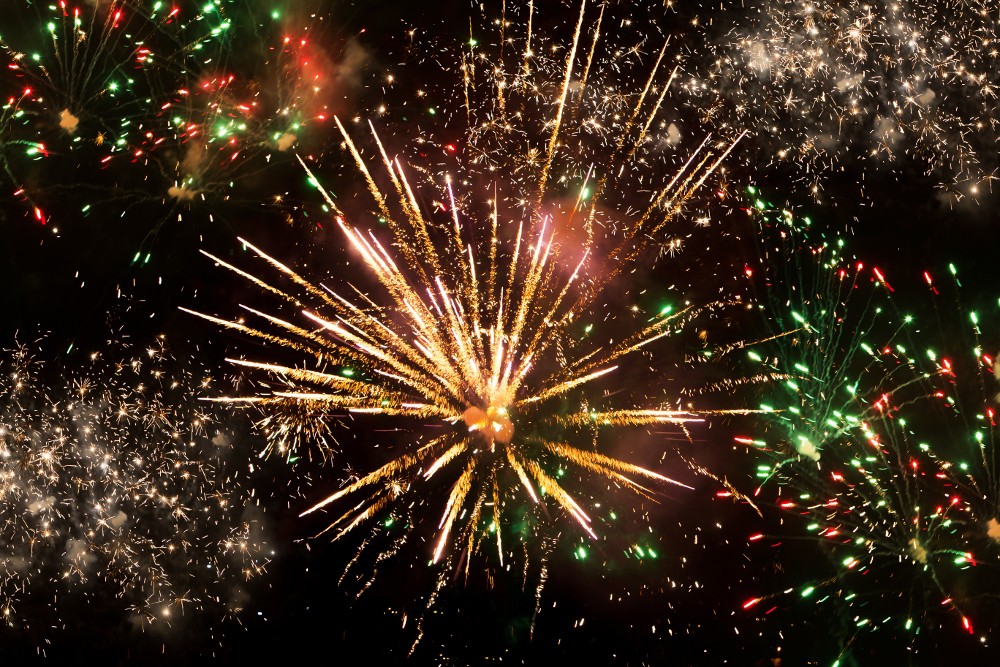
2.45 - 2.46 Up in flames Fireworks produce a whole range of different colours. All fireworks release energy in the form of heat energy and are therefore exothermic. Explosions and rocket power is provided by gunpowder and similar explosive mixtures. Colours are achieved by mixing compounds which contain various metal ions into the explo...
Defining salts Common "table" salt ( sodium chloride) is found dissolved in large quantities in seawater. Sodium Chloride is just one example of the many compounds which can be called salts. Most salts are crystalline ionic compounds A salt is defined as : A compound resulting from a chemical reaction of an acid, in ...
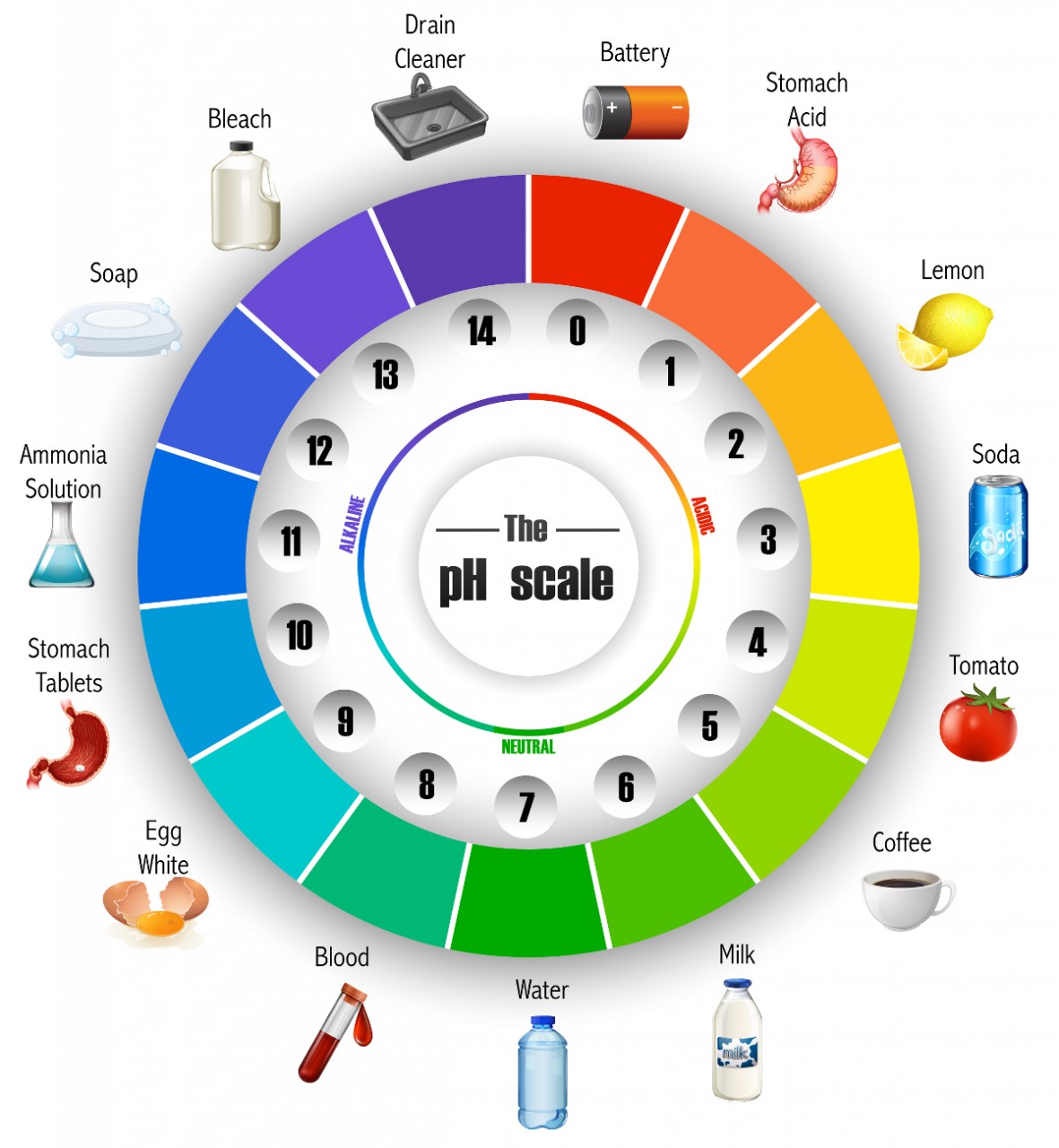
Acids and alkalis are all around us; many everyday foods, drinks, cleaning products are acidic or alkaline. Study the image of the pH scale "wheel". This scale gives a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. A value of pH 7 is regarded as neutral . Substances with a pH value greater than 7 are regarded as alkaline ...