Organic Reaction pathways OCRAQAEdexcel Aliphatic routes Aromatic routes Learn the reagents and changes
Introduction Water has no obvious smell. Water has no taste and water is colourless. Water has a neutral pH value ( pH 7). Many other chemical substances have similar properties . We therefore need to find a chemiscal test for water. Enter your text here ... When water is added to anhydrous (white) copper sulfate the copper s...
Intro image Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ... To test for carbon dioxide. the test is to force the sample that you believe may be carbon dioxide in to a solution of lime water. if the sample does contain carbon dioxide then the solution will turn cloudy, if it does not then the sample cannot contain carbon dioxide. Enter your text...
Oxygen is a very reactive gas. It makes up approximately 20% of our atmosphere. The standard test for oxygen is to place a glowing splint into a test tube that may contain the gas. If the splint glows brighter and/or relights into flame then it is a positive result for oxygen.
Introduction Hydrogen is a flammable gas. It burns in air to produce water. A convenient test for hydrogen is to put a lighted splint in the mouth of a test tube full of the gas . The gas will burn with a characteristic squeaky pop if hydrogen is present. Hydrogen gas can be used as a fuel. When hydrogen burns in air it combines with ox...
OCREdexcelAQA Transition elements : properties Ligands and complex ions Ligand substitution and precipitation Redox reactions Electron configurations The video here uses the relevant section of the Royal Society of Chemistry's periodic table website to show the electron configurations of the first row of the transition ...
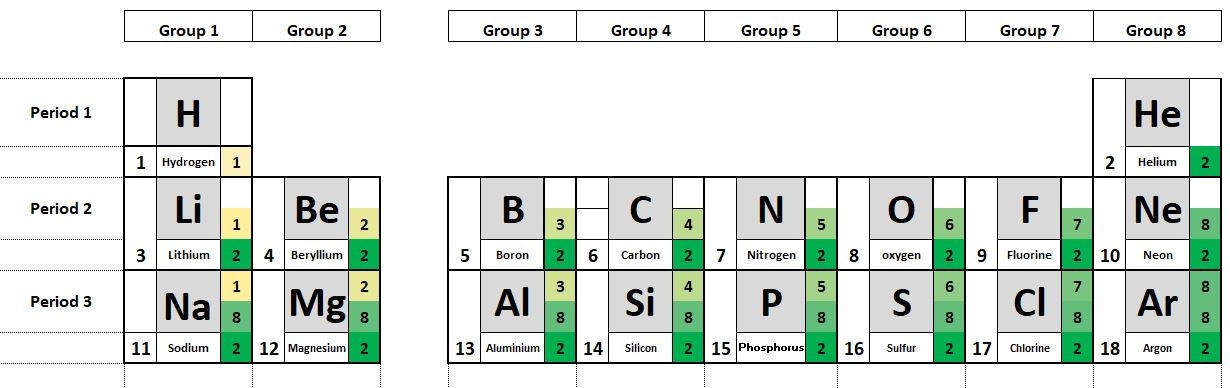
The elements in the periodic table are organised in order of increasing atomic number.
The elements in the periodic table are organised in order of increasing atomic number.
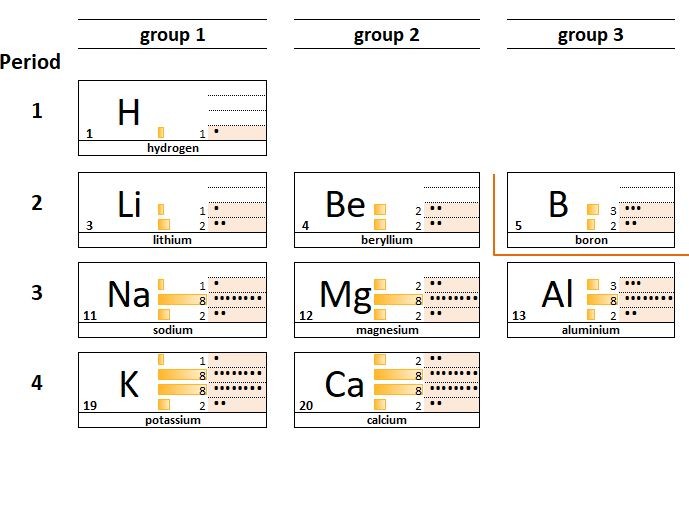
1.19 Deducing electron configurations Students should: 1.19 understand how to deduce the electronic configurations of the first 20 elements fromtheir positions in the Periodic Table A carbon atom has 6 protons and therefore 6 electrons. The electrons are arranged in two shells; 2 electrons in the first shell and 4 electrons in...
1.20 - 1.22 Activity 2. Periodic variations Students should: 1.20 understand how to use electrical conductivity and the acid-base character of oxides to classify elements as metals or non-metals 1.21 identify an element as a metal or a non-metal according to its position in the Periodic Table 1.22 understand how the electronic configura...
1.23 Family resemblances Hydrogen is often listed above group 1 the Alkali metals. Although like group 1 atoms, hydrogen atoms have a single electron in their outer shell, Hydrogen is not a metal. Students should: 1.23 understand why elements in the same group of the Periodic Table have similarchemical properties 1.24 und...
Carbonyl compounds all contain a C=O double bond. This is usually formed when an alcohol is oxidised using an oxidizing agent such as acidified sodium dichromate. The position of the C=O bond determines whether the compound is an aldehyde or ketone OCREDEXCEL Reactions of carbonyl compounds Enter your text here...
This animation allows you to see the electron arrangements which explain the formation of some double and triple bonds. Bond lengths and bond energy Here you can examine the effect that multiple bonds have upon the length of the bond. Use the top of the three buttons ( C-C ) to select the data for a carbon - ca...
First ionisation energiesInfogram Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ...
Crystallisation can be used to separate a solid solute from its solvent. Re-crystallisation is used to purify samples obtained in the laboratory. But what is a crystal?
Find out about fractional distillation ; why it is different from simple distillation and how it can be used industrially
Distillation is used to separate liquids from one another. Visit this page to see distillation in the laboratory and look at an industrial scale process.
Chromatography is another important separation technique. Several different types of chromatography exist.
Filtration can be a simple technique used to separate insoluble solids from a mixture or suspension. It has a lot of everyday applications.