1.27 The Mole
1.27 What is a mole? Students should: 1.27 know that the mole (mol) is the unit for the amount of a substance 1.28 understand how to carry out calculations involving amount of substance, relativeatomic mass (Ar) and relative formula mass (Mr) A mole (mol) is the quantity of anything that has the same number of particles as there are ato...
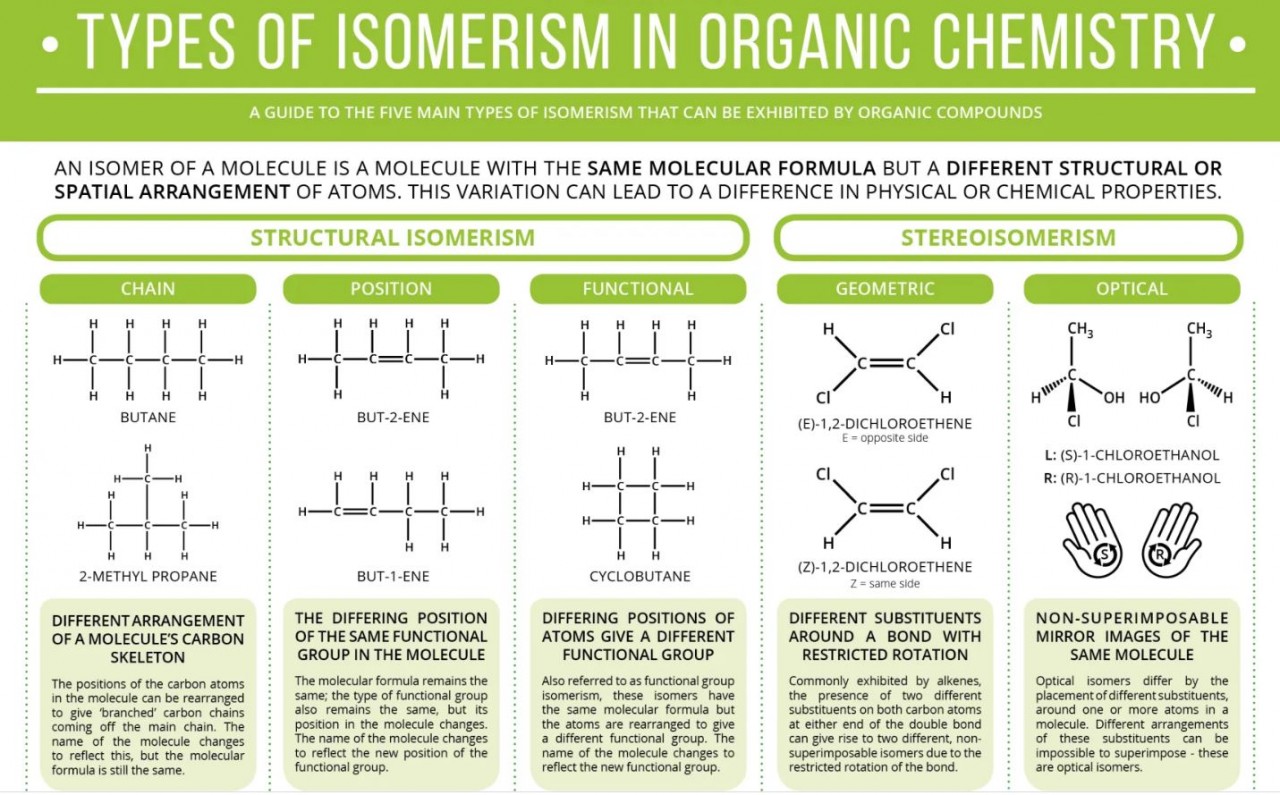
1.26 Formula masses
1.26 "Counting" by measuring mass Sometimes chemists need to "count" out a specific number of atoms, ions or molecules of a substance. Atoms are very very small - too small to see. It is therefore impossible to measure them out by counting individually. Instead we "count" them out by measuring their mass - much like ...
Copy of Copy of 1.26 - 1.28 Moles and mountains
Relative masses allow chemists to "count out" atoms and molecules so they can ensure that the appropriate amounts of substances are reacted.
Rusting rates
Intro image Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ... Enter your text here ...
Effect of particle size on the rate of rusting
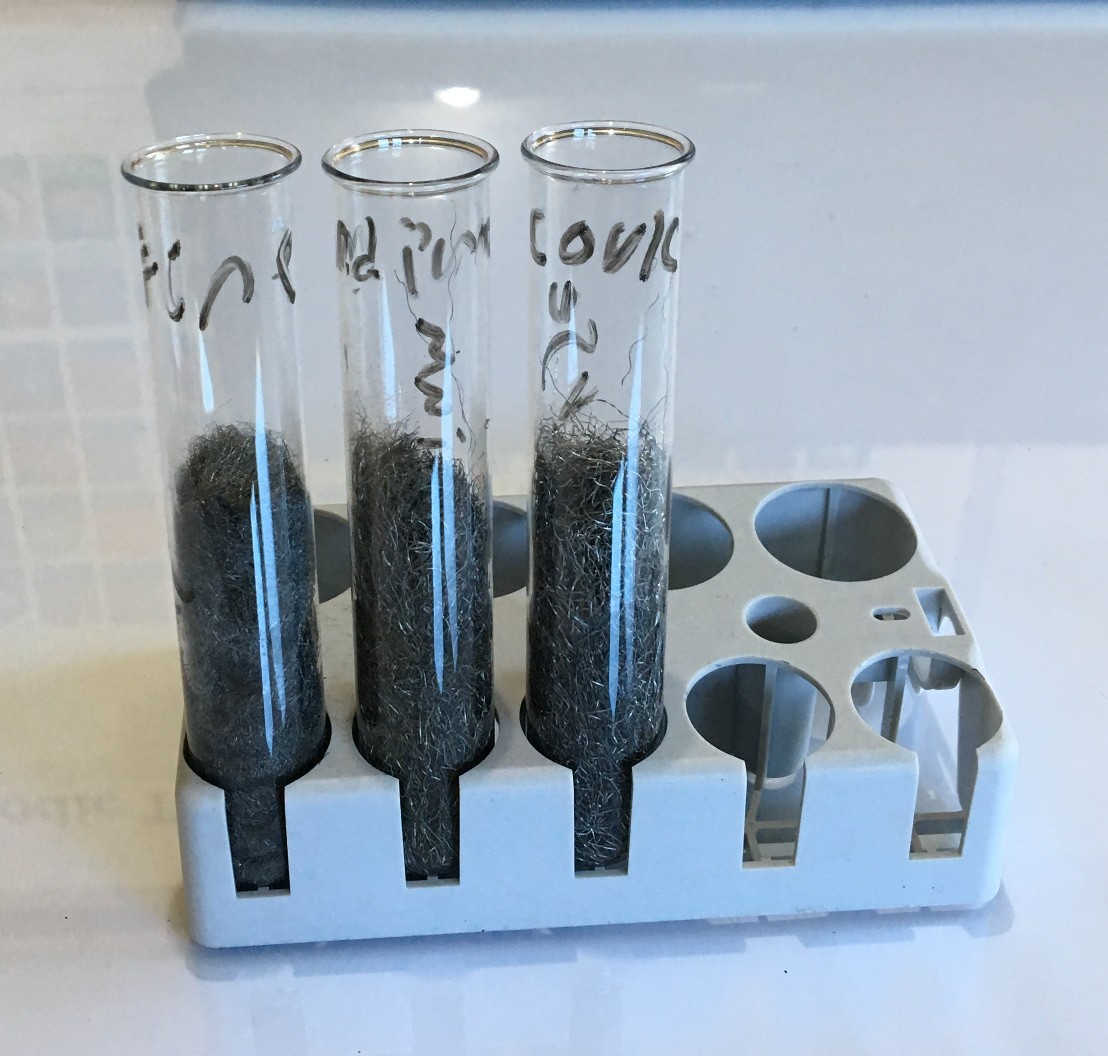
To test the effect of particle size on the rate of oxidation we prepared three samples of steel wool each with different levels of coarseness (shown left). The test tube on the left contains the fine steel wool while the one in the middle contains the medium conciseness steel wool and the test tube on the right contains the coarsest stee...