Practical techniques in organic chemistry
Synthesis and separation.
Purification methods.
Recrystallisation is a purification technique used to separate a solid compound from impurities by exploiting differences in solubility.
How it works
- Dissolve the impure solid in a hot solvent in which the desired compound is highly soluble at high temperature but poorly soluble at low temperature.
- Filter hot, if needed, to remove insoluble impurities.
- Cool the solution, causing the desired compound to crystallize out while soluble impurities remain in solution.
- Collect the crystals by filtration and dry them.
Purpose
- To obtain a pure solid from an impure sample.
- Commonly used in organic and inorganic laboratories to purify synthesized products.
In this video Professor Dave explains in some detail how to use this method and why it works.
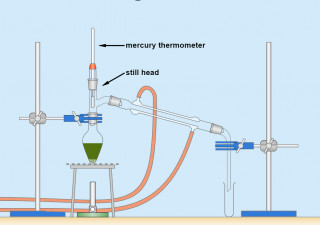
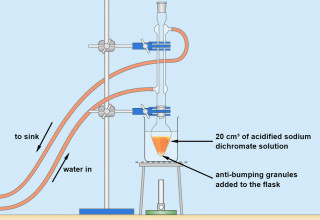
Synthesis of an Ester
Reflux
Enter your text here ...
Neutralisation
Enter your text here ...
Separation
Enter your text here ...
Drying
Enter your text here ...