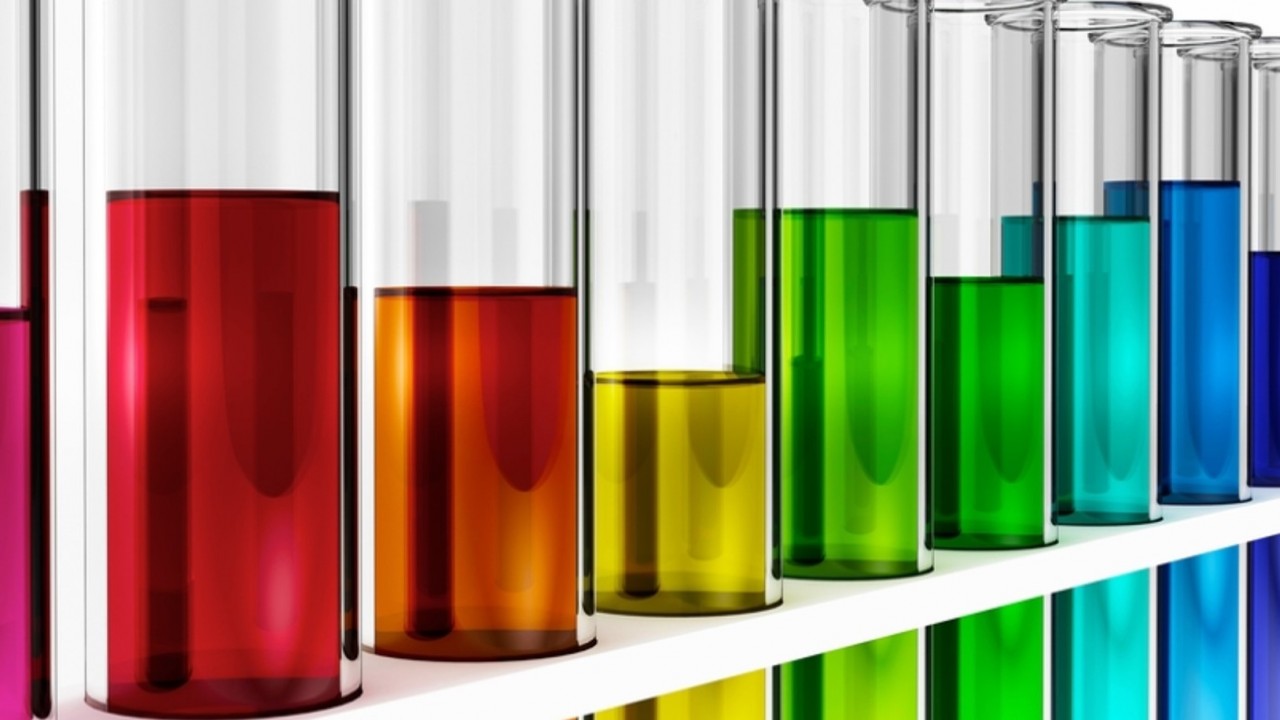
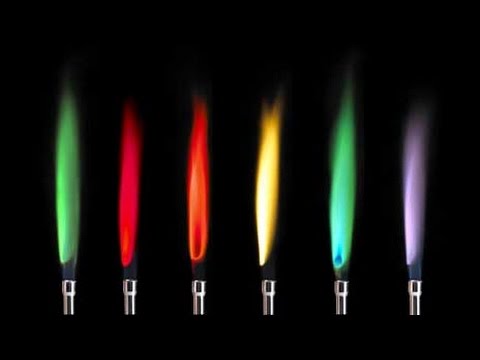
Flame tests can be used to identify some metal ions (cations).Lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium and copper compounds producedistinctive colours in flame tests:• lithium compounds result in a crimson flame• sodium compounds result in a yellow flame• potassium compounds result in a lilac flame• calcium compounds result in an orange-red flame• copper com...
2.15 - 2.20 Loss and gain Oxidation and reduction reactions are very commonplace. When a element combines with oxygen that element is said to have been oxidised. When the oxygen is removed from an oxide of an element to leave the element on its own, the oxide is said to have been reduced. Here we will use broader definition of oxidation ...
Ionic compounds form when the atoms of a metal combine with the atoms of a non - metal
Atomic models Atoms are the building blocks of matter. Atoms are the smallest possible particles into which an element can be subdivided, without changing its properties. As building blocks, they can be thought of spheres. However, to understand how and why atoms join up with one another, a more sophisticated model is needed....
Defining salts Common "table" salt ( sodium chloride) is found dissolved in large quantities in seawater. Sodium Chloride is just one example of the many compounds which can be called salts. Most salts are crystalline ionic compounds A salt is defined as : A compound resulting from a chemical reaction of an acid, in ...
Enter your text here ... IntroductionPearson specification A lot of everyday substances including some foods contain Acids. You can find alkalis amongst a number of common cleaning products. Acids are neutralised by alkalis to form salts and water. Here we consider the ways in which these reactions can be used...
4.34 - 4.37 From wine to vinegar Carboxylic acids are a homologous series of compounds with the functional group -CO2H. They are all organic acids and are regarded as weak acids which means they do not ionise completely in solution. Carboxylic acids are formed when alcohols are oxidised by the air or by using an appropriate ox...
3.1 Energetics Students should: 3.1 know that chemical reactions in which heat energy is given out are described asexothermic, and those in which heat energy is taken in are described as endothermic Every chemical reaction has an accompanying change in energy. Some reactions release energy to the surroundings and are known as Exothermic...
4.23 Meet the alkenes The Alkenes are another Homologous series of Hydrocarbons. They differ from the Alkanes because they contain in their molecules at least one double bond between two of the carbon atoms. Because of their double bonds, the alkenes are more reactive than the alkanes and thus they are useful for making new compound...
in this topic, we have looked at the way in which substances form different structures. The type of structure formed depends on the type of bonding: Three types of bonding are. metallic, covalent and ionic. metallic: formed when metals bond with themselves or other metals. covalent: formed when non-metal bonds with itself or another...