2.9 - 2.13 Gases in the atmosphere
Oxygen is a key component of the atmosphere and is critical for the support of life. Its reactivity makes it essential for respiration and combustion reactions - both of which release energy.
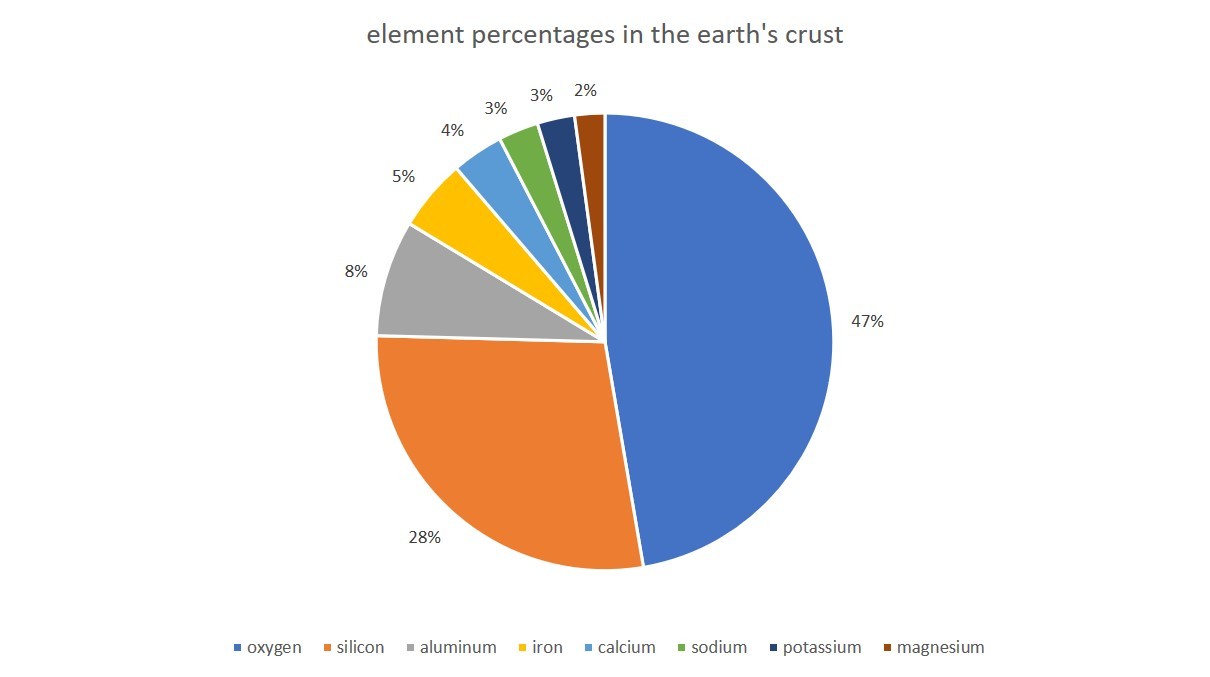
Oxides are formed when oxygen combines with other elements. Much of Earth's crust (48.5% by mass) is composed of oxygen in the form of oxides
- Which element is the most abundant in the Earths crust?
- Which of the elements shown is the least abundant.
- Why is the element gold not shown in the data?
- What is the total of all the percentages given?
- Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth's crust.
- Magnesium is the least abundant element in the earth's crust
- The percentage of Gold in the earth's crust is not significant enough to be noticed.
- 100%
2.9 Activity 1. The compositon of Air
Students should:
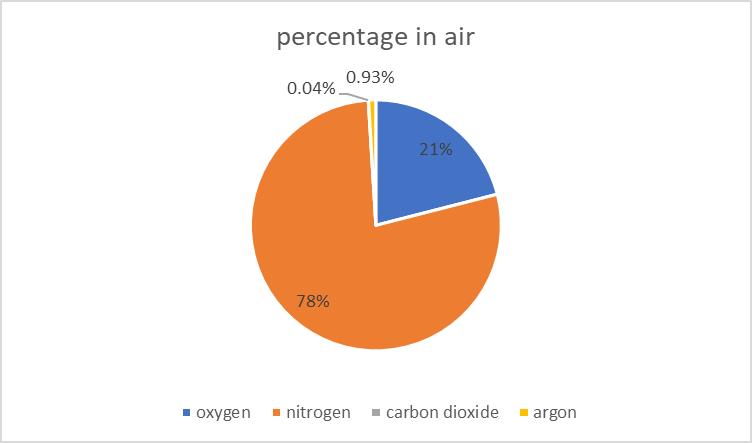
- 2.9 know the approximate percentages by volume of the four most abundant gases in dry air
| Name of Gas | Formula | Relative molecular mass | percentage | comment |
| Name of Gas | Formula | relative molecular mass | percentage | comment |
| oxygen | O2 | 16 | 21% | supports combustion and respiration |
| nitrogen | N2 | 14 | 78% | N2 - triple bond |
| argon | Ar | 40 | 0.93% | argon is a colorless, odorless, inert gas |
| carbon dioxide | CO2 | 44 | 0.04% | carbon dioxide is incombustible |
Students should:
- 2.10 understand how to determine the percentage by volume of oxygen in air using experiments involving the reactions of metals (e.g. iron) and non-metals (e.g. phosphorus) with air
Initial volume = 115. Final volume = 91.
| Initial volume/ml | Final volume/ml | Volume change/ml |
| 115 | 91 | 24 |
Volume change = 24.
percentage change = (24 / 115) * 100 = 21%
Conclusion: 21% of the atmosphere is oxygen
Students should:
- 2.11 describe the combustion of elements in oxygen, including magnesium, hydrogen and sulfur
- What do they mean by "valence" electrons.
- Describe the reaction between magnesium and oxygen.
- What are the properties of the oxide formed.
- Describe the reaction between sulfur and oxygen.
- What is the name of the oxide formed?
- What sort of properties does the oxide of sulfur have?
- Describe the combustion of hydrogen in oxygen. use the link below if you need to:
5 Awesome Hydrogen Explosions! - YouTube
Craig Beals shares five of his favorite hydrogen explosion demonstrations including the exploding Hydrogen Balloon, Pringles Hydrogen Rocket, Plastic Bottle ...
- The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell
- Magnesium and oxygen combine to form a white magnesium oxide residue
- The magnesium oxide dissolves in water to produce an alkaline solution
- The sulfur melts then combines with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide. Sulfur dioxide dissolves in water to form sulfurous acid
- Sulfur dioxide is formed when sulfur burns in the air
- Oxides of sulfur are acidic
- Hydrogen burns explosively in oxygen to produce water
Students should:
- 2.12 describe the formation of carbon dioxide from the thermal decomposition of metal carbonates, including copper(II) carbonate
- 2.13 know that carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas and that increasing amounts in the atmosphere may contribute to climate change